Proteins are molecules that carry out multiple fundamental functions in each cell. Made up of a series of linked amino acids, the makeup of each protein dictates its structure which then determines its function.
Peptides are a short series of amino acid residues that are linked together by peptide bonds. Short peptides have been shown to play an important role in regulating gene expression, and in restoring the damaging genetic changes that occur with age. These peptides are signaling molecules that act as regulatory factors through their interactions with DNA and histone proteins.
Understanding peptide therapy
Peptide therapy is the use of targeted signaling amino acid chains to instruct cells on the functions they need to perform. The physiological process of aging is highly influenced by the regulation of homeostasis and is related to the aging of cells, tissues, and organs.
Short peptides have been demonstrated to play an important role in modulating transcription, the transmission of biological information, and in restoring the genetic alterations that occur with aging.
Although the content of peptides is similar between cells, the structure and function of each cell defines the content of its biologically active substances and its unique ultrastructures. Moreover, certain biologically active substances are predominantly synthesized or accumulated in specific tissues.
Nano Organo Peptides (NOPs) are 3nm in size and have a molecular weight of less than 10kDA and are derived from organ-specific cells. Mito Organo (MO) peptides are biologically extracted mixtures of cellular peptides that have predominantly mitochondria-specific functions. As part of the aging process, the volume and strength of signals to the mitochondria declines, causing signals to be sent back to the nucleus to arrest stop cells reproducing and initiate cell death. MO peptides are organ-specific extracts that are aimed at revitalizing and rejuvenating mitochondrial activity, thereby regenerating cells and organisms.
Our NOPs and MOs are manufactured by European Wellness Biomedical Group at the EW facility in Europe, who are committed to ensuring that all organopeptide products are pathogen-free and safe. These organopeptides are being used rejuvenate and improve health. We partner with top-tier research institutions, universities and manufacturing facilities to provide data on the effectiveness of organ-specific peptides’ ability to rejuvenate and heal.
Despite the numerous studies highlighting the therapeutic effectiveness of NOP and MO peptides and the established procedures documented on obtaining them, little is known of the exact makeup of these formulations.
Mass spectrometry (MS) has been shown to identify and quantify these peptides and is thought to be able to identify the peptides derived from peptides obtained from cells. The mass spectrometer produces a readout of peaks plotted in relative abundance against the mass-to-charge ratios.
Source
Alicia Wells, Adam Good, Kimia Damyar, Michael Alexander, Jonathan RT Lakey, et al., Mass Spectrometry Analysis of Novel Stem Cell-Derived Peptides. Am J Biomed Sci & Res. 2022 – 16(2). AJBSR.MS.ID.002215. DOI: 10.34297/AJBSR.2022.16.002215
In a recently published study in the American Journal of Biomedical Science & Research [1], our scientists have outlined the experimental methods and the results from performing MS on various EW peptides to characterise them. The purpose of this study was to identify the composition of the unknown peptide solutions in their cellular-derived formulations.
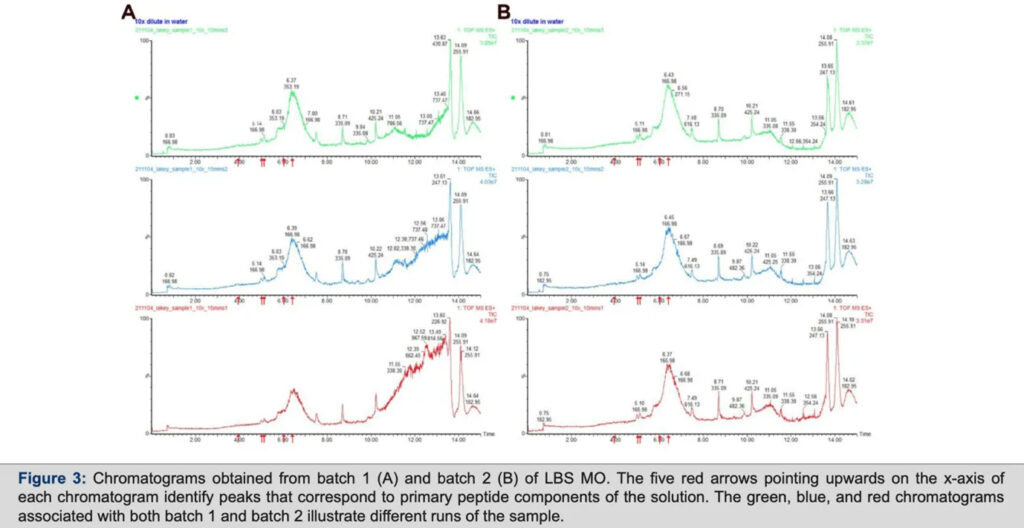
The paper outlines the experimental methods and the results from performing MS on various peptides from European Wellness Biomedical Group (EW). The results of our study using MALDI-TOF to analyze 8 samples of EW peptides.
The experimentally derived peaks were searched against a database of known proteins to identify the peptides present in each sample. Our results indicated that there were no statistically significant differences in protein concentration (ug/ mL) between batches and that five major peptide products tested, and we were able to identify major peptide peaks.
Though further research is required in larger sample sizes, this study increases our understanding of the characterization of the peptides and proteins within our organopeptides products. This important scientific work will ultimately help deliver better patient outcomes in treating aging and other diseases.
References
Alicia Wells, Adam Good, Kimia Damyar, Michael Alexander, Jonathan RT Lakey, et al., Mass Spectrometry Analysis of Novel Stem Cell-Derived Peptides. Am J Biomed Sci & Res. 2022 – 16(2). AJBSR.MS.ID.002215. DOI: 10.34297/AJBSR.2022.16.002215